Most Popular
Why Hair Transplant Surgery is Risky
Keep in mind the risk of hair transplant surgery.Anesthesia. Adverse systemic reactions to local anesthetics fall into four categories: toxic, psychoactive, ... ...


Why Hair Transplant Surgery is Risky
Rated: 
 , 0 Comments
, 0 Comments
Total hits: 599
Posted on: 09/06/22
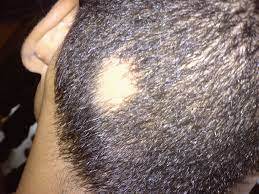
Keep in mind the risk of hair transplant surgery.
Anesthesia.
Adverse systemic reactions to local anesthetics fall into four categories: toxic, psychoactive, autonomic, or allergic. The vast majority of adverse reactions to local analgesics are psychological in nature and associated with fear. A true immunological reaction to a local anesthetic is rare. Even if the patient has received local anesthesia in the past, we recommend that everyone undergo a sensitivity test. Hair transplant in Delhi is risky but not dangerous
Intraoperative complications:
Tachycardia may occur with the introduction of tumescent fluid containing adrenaline. It is usually transient. However, in a patient with heart failure, it may pose a risk. Therefore, all patients, especially those over 40 years of age, are shown an electrocardiogram and a medical assessment of suitability for anesthesia. It is also recommended to monitor heart rate and blood pressure throughout the procedure, especially during the administration of anesthesia.
Postoperative complications:
Fainting is a complication that often occurs at the end of an operation, especially if it is a long operation. This may be due to pain, postural hypotension, xylocaine (HBV Medi Sciences Ltd., Uttarakhand, India) toxicity (which may be associated with seizures), inadequate hydration, hypoglycemia, etc. Appropriate anesthetic and analgesic precautions are recommended, and use of Xylocaine is minimized by completing the operation as soon as possible. Maintaining hydration and electrolyte balance during surgery, avoiding sudden changes in posture (such as standing up suddenly), and administering clonidine (which has anticholinergic and analgesic activity) prior to surgery may help reduce the chance of fainting. can be found.
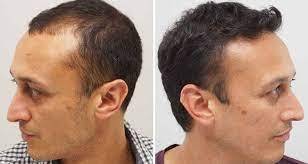
- Pain is a common complication during and after surgery and can be easily managed with proper surgical technique and use of analgesics. Factors contributing to pain include prolonged sessions with a wide bandage, bleeding, tension in the wound, and insufficient anesthesia. Field blockade with local anesthesia mixed with adrenaline is the standard procedure. In addition, ice packs and vibrators can also be used to reduce pain during an anesthetic injection (vibraesthesia). Adequate relief of postoperative pain can be achieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other analgesics.
- Postoperative edema may occur in the recipient area. To reduce this, you can use oral steroids in the postoperative period.
- Postoperative pruritus is common in both the donor and recipient areas. This may cause drying and crusting. Applying salt spray several times for 3-4 days can reduce itching. Shampooing can help in controlling the itching effectively. In addition, oral antihistamines can help with itching, and dryness can be addressed with topical aloe vera.
- Postoperative hiccups or cough is another rare but significant complication as it can last for 2-3 days. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to stimulation of the sensory divisions of the C2, C3, and C4 nerves, which also innervate the diaphragm via the phrenic nerve.
- Infection: Local infection can occur in both the recipient area and the donor area. The incidence of mild to severe infection is rare (<1%), which may be due to poor hygiene, excessive crusting, or a pre-existing medical risk factor. Closing the donor site with high tension, leading to circulatory failure and severe crusting, can increase the risk of infection. Recipient site infections often present with papulo-pustules localized in the affected area. Occasionally, there will be palpitations, erythema, and tenderness indicating abscess formation at the graft site or in a localized area along the incision line. Sepsis has also been reported after hair transplantation.
Comments
There are still no comments posted ...
Rate and post your comment